Detailed Analysis of Each Level of Maslow’s Hierarchy
As you navigate through the intricate layers of Maslow's Hierarchy, you'll uncover a fascinating journey of human needs and motivations. Starting from the fundamental physiological necessities, each level builds upon the foundation laid by the previous one, shaping individuals' behaviors and aspirations. By unraveling the complexities of each tier, a profound understanding of human nature and fulfillment emerges, shedding light on the intricate interplay between basic survival instincts and higher aspirations. Stay tuned to explore the profound implications of Maslow's Hierarchy on personal development and psychological well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Physiological needs include food, water, shelter, air, and sleep for survival.
- Safety needs involve security, stability, and risk assessment to minimize threats.
- Belongingness needs encompass social connections and relationships for community support.
- Esteem needs relate to recognition, respect, and self-worth for well-being.
- Interconnectedness of needs levels shows progression from lower to higher needs for motivation.
Overview of Maslow's Hierarchy
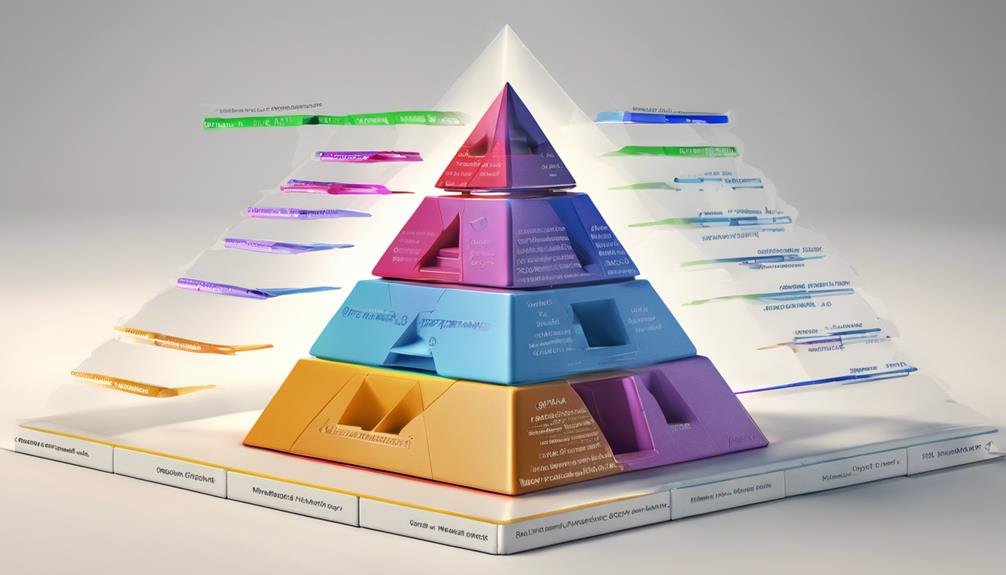
Analyzing Maslow's Hierarchy reveals a structured framework that categorizes human needs into distinct levels of importance. This hierarchy, proposed by psychologist Abraham Maslow, outlines five levels of needs that drive human motivation and personal growth.
At the base of the pyramid are physiological needs, such as air, water, food, and shelter. Once these basic needs are met, individuals move on to the next level, safety needs, which involve seeking security and stability.
As individuals progress up the hierarchy, they encounter belongingness and love needs, which emphasize the importance of social connections and relationships for mental health and well-being. Moving further up, esteem needs come into play, focusing on gaining recognition, respect, and self-worth.
Finally, at the pinnacle of Maslow's Hierarchy are self-actualization needs, which involve reaching one's full potential and achieving personal growth.
Understanding Maslow's Hierarchy is essential in comprehending psychological development and the factors that drive human behavior. By recognizing and addressing these different levels of needs, individuals can aim towards holistic growth and fulfillment.
Physiological Needs Analysis
Physiological needs form the foundational level of Maslow's Hierarchy, encompassing essential requirements for human survival and well-being. These basic requirements are essential for sustaining life and carrying out essential functions. Food, water, shelter, air, sleep, and other physiological needs are fundamental for maintaining bodily functions and overall health. Without meeting these basic requirements, individuals may experience physical discomfort, illness, and even risk their lives.
Food and water are important for providing the body with necessary nutrients and hydration to function effectively. Shelter protects individuals from environmental elements and provides a safe space for rest and recuperation. Adequate sleep is crucial for physical and cognitive health, allowing the body to rejuvenate and repair itself. Additionally, access to clean air is essential for respiratory functions and overall well-being.
Meeting these essential functions ensures that individuals can progress to higher levels of Maslow's Hierarchy, focusing on fulfilling safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
Safety Needs Exploration
In understanding Maslow's Hierarchy Levels, delving into the exploration of safety needs reveals essential aspects of human behavior and well-being. The concept of safety needs encompasses more than just physical safety; it includes the need for a sense of security in various aspects of life. Individuals seek stability and predictability in their environment to fulfill these needs. An important factor in addressing safety needs is the process of risk assessment. People continuously evaluate potential threats to their safety, whether they're physical, emotional, or financial. This risk assessment mechanism influences decision-making and behavior, as individuals work to minimize perceived dangers and maximize feelings of security.
Furthermore, the fulfillment of safety needs can have a significant impact on an individual's overall psychological well-being. Lack of security can lead to heightened levels of stress, anxiety, and fear, affecting mental health adversely. Creating environments that promote a sense of safety and security is essential for fostering personal growth and self-actualization according to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Understanding Belongingness Needs
Exploring the fundamental human need for belongingness reveals intricate social dynamics and emotional connections that play a pivotal role in shaping individual identity and well-being. Belongingness research delves into the intricate fabric of human interactions, highlighting the significance of social connections in fostering a sense of community and acceptance. Studies in this field emphasize the importance of relationships, whether familial, romantic, or platonic, in fulfilling our innate desire for belongingness.
Social connections analysis further underscores the impact of belongingness on mental health and overall life satisfaction. Research shows that individuals with strong social support systems tend to experience lower levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, a sense of belongingness is closely linked to increased self-esteem and resilience in the face of challenges.
Understanding the intricacies of belongingness needs provides valuable insights into the complexities of human behavior and psychology, shedding light on the profound influence of social connections on our well-being and sense of self.
Esteem Needs Examination
Delving into the examination of esteem needs reveals the intrinsic human desire for recognition, respect, and self-worth within social and personal contexts. Self-esteem assessment plays an important role in understanding how individuals perceive themselves and their value in society. It involves evaluating one's feelings of competence, achievement, and respect from others.
Esteem needs satisfaction is essential for fostering a healthy self-image and developing a sense of confidence and pride in one's abilities.
Research indicates that individuals who receive consistent positive feedback and recognition tend to have higher self-esteem levels compared to those who lack validation. Additionally, fulfilling esteem needs not only boosts individual well-being but also enhances overall productivity and motivation.
Understanding the dynamics of esteem needs can help individuals navigate social interactions more effectively and build stronger relationships based on mutual respect.
Unpacking Self-Actualization
As you explore Self-Actualization, you'll encounter a set of distinct characteristics that distinguish individuals who've reached this pinnacle of personal growth.
Factors such as creativity, acceptance of reality, spontaneity, and a sense of purpose play significant roles in the journey towards Self-Actualization.
Understanding these traits and the external influences that can impact one's progress in achieving self-fulfillment is essential for a thorough analysis of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Characteristics of Self-Actualization
Essentially, self-actualization, the pinnacle of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, is characterized by a profound sense of self-awareness and personal growth. It represents the realization of one's full potential and the continual pursuit of personal growth and fulfillment. Individuals who've reached the state of self-actualization demonstrate a deep understanding of themselves, their values, and their unique place in the world. This level is marked by a strong desire for personal development and a commitment to realizing one's individual potential.
Self-actualized individuals exhibit a high level of autonomy and are driven by intrinsic motivations rather than external rewards. They're often creative, spontaneous, and open to new experiences, constantly seeking ways to expand their knowledge and understanding of the world.
Personal growth and self-improvement are lifelong pursuits for those who've achieved self-actualization, as they're committed to continual self-exploration and development. Ultimately, self-actualization is a journey towards realizing one's true self and living a life that's authentic, meaningful, and fulfilling.
Factors Influencing Self-Actualization
Understanding the intricate interplay of various internal and external factors is essential in unraveling the complex dynamics that influence the process of self-actualization. Self-actualization is deeply intertwined with intrinsic motivation, the internal drive that compels individuals to pursue personal development and achieve their fullest potential.
Factors influencing self-actualization encompass a broad spectrum, ranging from psychological needs to external influences. Intrinsic motivation plays a pivotal role in self-actualization, as individuals driven by internal desires rather than external rewards are more likely to initiate a journey of personal growth and fulfillment.
Personal development, a core aspect of self-actualization, involves continuous self-improvement, introspection, and the pursuit of meaningful goals aligned with one's values and beliefs. External factors such as a supportive environment, access to resources, and opportunities for growth can also notably impact an individual's path to self-actualization.
Interconnection of Needs Levels
The interconnection of needs levels in Maslow's Hierarchy reveals a complex web of dependencies that influence an individual's motivation and behavior. Maslow's hierarchy connection illustrates how the fulfillment of lower-level needs forms the foundation for progressing towards higher-level needs.
Each level of the hierarchy is interconnected, with the satisfaction of one level paving the way for the activation of the next. For instance, meeting physiological needs such as food and shelter is essential before focusing on safety needs like job security.
This hierarchical structure highlights the needs hierarchy interdependence, emphasizing that neglecting one level can disrupt the individual's overall well-being and motivation. Understanding these interconnections can help individuals identify which needs are unmet and prioritize their efforts accordingly.
Implications for Personal Growth
To achieve personal growth, self-actualization, the pinnacle of Maslow's hierarchy, is essential. This involves realizing your full potential and working towards continual self-improvement.
Self-Actualization for Growth
Self-actualization serves as the pinnacle of Maslow's hierarchy, representing the drive for personal growth and fulfillment at the highest level of human motivation. It encapsulates the concept of achieving one's full potential and becoming the best version of oneself.
This stage involves a deep exploration of one's capabilities, interests, and values to lead a life that's authentic and purposeful. Personal development at the self-actualization level goes beyond meeting basic needs; it involves continuous self-improvement, creativity, and a strong sense of autonomy.
To reach self-actualization, individuals must be motivated by intrinsic desires and a commitment to personal and professional growth. This level of the hierarchy emphasizes the importance of pursuing goals that are in line with one's true self and values, leading to a profound sense of fulfillment and contentment.
Meeting Basic Needs
Exploring the foundation of Maslow's hierarchy, understanding how meeting basic needs influences personal growth is essential in comprehending the progression towards self-actualization. Basic needs are fundamental requirements for human survival and include physiological needs like food, water, shelter, and safety.
When these basic needs are met, individuals can focus on higher levels of personal growth and development.
The significance of meeting basic needs can't be overstated. Without fulfilling these foundational requirements, individuals may struggle to advance in other areas of their lives. Research indicates that when basic needs are unmet, it can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and a sense of instability, hindering personal growth.
In contrast, when basic needs are satisfied, individuals are more likely to feel secure and have the mental and emotional capacity to pursue self-improvement.
Psychological Needs Fulfillment
Understanding the fulfillment of psychological needs is paramount in deciphering the implications for personal growth within the framework of Maslow's hierarchy levels. Psychological needs encompass aspects essential for mental health and well-being. These needs involve feeling a sense of belonging, having strong social interactions, and fostering self-esteem.
When these needs are met, individuals are more likely to experience personal growth and self-actualization.
Mental health plays a critical role in psychological needs fulfillment. It involves maintaining emotional stability, coping with stress effectively, and having a positive self-image. By addressing mental health concerns and ensuring psychological needs are met, individuals can pave the way for personal growth.
Social interaction is another key component of psychological needs fulfillment. Engaging in meaningful relationships, forming connections, and feeling a sense of community are essential for overall well-being. These interactions contribute significantly to personal growth by providing support, fostering communication skills, and enhancing emotional intelligence.
Application in Psychology
Applying Maslow's Hierarchy levels in psychology involves identifying and analyzing how individuals' basic needs and motivations influence their behavior and well-being. In clinical applications, psychologists utilize Maslow's theory to understand the underlying reasons for an individual's psychological issues.
Research studies have shown correlations between unmet needs at various levels of the hierarchy and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. Therapeutic interventions often incorporate Maslow's principles to help clients progress towards self-actualization. Counseling techniques may involve addressing deficiencies in basic needs before delving into higher-level motivations.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of Humanistic Psychology demonstrated how integrating Maslow's Hierarchy into therapy sessions improved treatment outcomes for clients dealing with trauma. By focusing on fulfilling basic needs first, therapists can create a more stable foundation for addressing deeper emotional concerns.
These findings highlight the practical relevance of Maslow's theory in psychological practice, emphasizing the importance of considering individual needs and motivations in therapeutic settings.
Impact on Motivation
An in-depth analysis of Maslow's Hierarchy levels reveals a significant impact on individuals' intrinsic motivations and drive towards personal growth and fulfillment. Understanding the hierarchy's influence on motivation is essential for comprehending human behavior and driving factors. Maslow's theory suggests that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before progressing to higher-level ones.
This hierarchy analysis highlights how fulfilling physiological and safety needs can directly impact an individual's motivation to aim for love and belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization.
Motivation impact is evident as individuals who've their basic needs met are more likely to be motivated by growth, achievement, and self-improvement. This insight can be vital for educators, employers, and individuals seeking personal development. By recognizing where individuals lie within the hierarchy, tailored approaches to motivation and goal-setting can be implemented.
The hierarchy analysis not only sheds light on individual motivations but also emphasizes the importance of creating environments conducive to personal growth and fulfillment.
Conclusion
To wrap up, endeavoring into the intricate layers of Maslow's Hierarchy reveals the intricate tapestry of human needs and motivations.
By understanding the progression from basic physiological needs to the pinnacle of self-actualization, individuals can navigate their own personal growth journey.
Just as Maslow's pyramid symbolizes the ascent to self-fulfillment, each level offers insights into the complexities of human behavior and psychology.
Embrace the challenge of self-discovery and work towards reaching your highest potential.